Cosmology
Cosmos CosmologyCosmology, i.e. the study of the cosmos, is a branch of astronomy that deals with the origin of the universe from the big bang all the way to the present and into the future, it's a study of the large scale characteristics of the known universe, to build upon our existing knowledge and formulate theories as to explain the origin of everything in its literal sense, this science deals with giving explanations for why and how the universe is the way it is as opposed to astronomy which is mainly concerned with observing and measuring phenomena and objects in the heavenly plain.
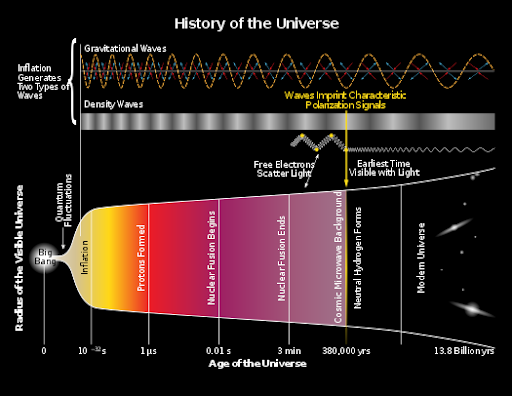
History of The Cosmos
Cosmology comprises mainly physical cosmology and observational cosmology. Physical cosmology deals with different cosmological models which shed light on the origin, evolution and the eventual and ultimate fate of the universe. Physical cosmology is instrumental in describing some of the largest-scale structures of the universe, from macroscopic galaxy clusters containing thousands of galaxies to “cold spots” on the cosmic microwave background map signifying more nothingness than usual in the eternal oblivion of space and time.
The modern iteration of true physical cosmology was heralded by Einstein’s theory of general relativity which explained gravity as a product of the universe's geometry and that any amount of mass produces a curvature in the very fabric of space and time. Physical cosmology has given us great insights on fundamental questions like “Is the universe expanding?”(spoiler alert: it is), “What is dark matter”, etc.
How can you become a Cosmologist?
To be a cosmologist, one has to have patience and adaptability as often experiments may not conform to the values expected from theories. Usually, one has to be resourceful and adapt one's work per needs. Knowledge of specialized software and equipment is important, and various computer programs run data analysis and simulation. An aptitude for mathematics and proper communication skills is also a must. In terms of job opportunities, a PhD in a related field is necessary and a strong base in mathematics. A post-doc research position is also heavily recommended; a cosmologist must have a tremendous eye for detail and be able to make proper conclusions from one's observations.
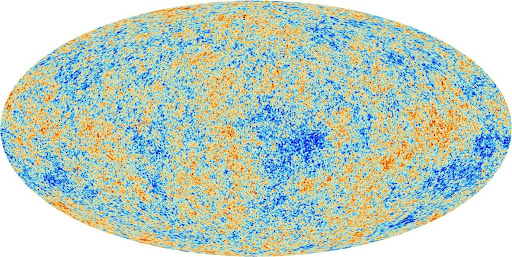
Observational cosmology is what sets modern cosmology apart from cosmology in the past
which was mostly based on conjecture and theories, as well as a healthy and unhealthy mix of religion and
philosophy. Today we are able to perform sophisticated measurements of the universe and measure stellar distances
with some degree of accuracy using parallaxes. We can even measure inter galactic distances using a complex set
of techniques known as the cosmic distance ladder.
This branch of cosmology has been instrumental in proving and disproving theories about the origin and nature of the universe, theories on dark matter,
the big bang, the expansion of the universe and the size of the universe. There was once a debate in the 1920s about whether the universe was only as
big as the milky way, known as the Shapely-Curtis debate, which was also settled by observational cosmology.
Experiments on cosmology are almost entirely done in the field of observational cosmology, while its ramifications on the properties of the universe are dealt with, in detail, by physical chemistry. Experimentation and observation is mainly done by observing the universe using satellites, telescopes etc, detecting gravitational waves using sophisticated equipment such as the LIGO observatory, observations of gravitational lensing have also helped to shine light on pre-existing theories and validate them such as the cosmic inflation theory, the big bang theory etc, more over observation of redshifts in galaxy clusters have allowed us to understand the fact that the universe is expanding, with the ability to observe the universe with much larger precision than ever before and with the validation of so many theories, the current era is popularly called the golden age of cosmology.
The physical nature of the said measurements are extremely diverse, ranging from “simple” space telescopes to billion dollar monochrome intersecting lasers which are used to detect gravitational waves resulting from collision between super massive blackholes billions of light years away which produce minute contractions in space which are of the order of 10-30 and thus cause said lasers to interfere with one another and thus produce a very minute and measurable change indicating the existence of gravitational waves.

Observations on gravitational lensing have also shed light on the existence of dark matter as well as dark energy which fuels the ever-accelerating expansion of the universe. SUPERBIT i.e. Super-pressure Balloon-borne Imaging Telescope is kept in the stratosphere above 99.2% of the Earth’s atmosphere, its primary aim is to provide insight into the distribution of dark matter in galaxy clusters, it is expected to produce results to the level of clarity obtained from the Hubble space telescope and can complement up and coming satellites such as the James Webb telescope. SUPERBIT is scheduled to be launched in March 2022.